Is BUTT JOINT Technology Better option for Overlapping?

Is BUTT JOINT Technology Better option for Overlapping?
Lapping the bars is traditional method in construction industry to transfer the structural load. It requires a significant amount of time to overlap two rebars So, it slows down the construction work.
Lapping the reinforcement has numerous drawbacks, which ultimately makes construction uneconomical and time consuming.
Problem with Overlapping?
Overlapping means the extra length in reinforcement bars. Two bars length overlapped and tie with the steel wires, some problem related to overlapping are discussed below:
· As per IS 456:2000 [Clause:26.2.5.1] Amendment No. 3 August 2007 states that “Lap splices shall not be used for bars larger than 32 mm. Bars larger than 32mm shall be welded or mechanically spliced.”
· During the lapping 1:6 slope provides referred as joggling of bars, it is quite difficult to maintain at site.
· Staggering: maintaining of staggering in lapping is not easy because as per (IS:13920 Clause-7.3.2.2 Page No-9) overlapping need to be maintained in mid H/2 height of column.
· As per IS 456:2000 [ Clause26.2.5 Page-44] suggesting that more than 50% of the bar should not be overlapped at a single location. If we overlap more than 50% bars at a location, then in case of an earthquake high-stress concentration at that location, and due to that joint failure chances are very high.
· Area of Column Size reduced as dead load reduces when we use overlapping in column maximum 4% reinforcement can be provided and 6% at location of overlapping is allowed.
· Overlapping of bars depends upon grade of concrete i.e., overlap doesn’t have own strength it depends on concrete strength.
Every Problem has a Solution!
There is a code IS 9417-2018 that governs the welding guidelines and some welding process of high strength deformed steel bars.
· Butt Joint Method
· Shielded Metal Arc Welding Process
· Gas Pressure Welding Process (GPW)
· Lap Welding process
· Gas metal arc welding process
If talk about mass production of welded joints, then Butt Joint is the most suitable method. Apart from mass production Butt Joint has numerous advantages over other methods.
How Butt Joint unique?
· No electrodes used, no gas required to melt the bars, only electric current is needed.
· No filler material is used, as parent is used to join the rebars.
· No need to cut the rebars in specified angle.
· Less time consuming.
What IS Code Says?
· As per IS 456:2000 [Clause 12.4 Page No.26] Welded joints or mechanical connections in reinforcement may be used but tests shall be made to prove that the joints are of the full strength of bars connected. Welding of reinforcements shall be done in accordance with the recommendations of IS 9417:2018.
· As per SP: 34 [APPENDIX A, Page No.209] Welded joints are permitted in reinforcement (mild steel and deformed bars).
· As per ACI-318-19 [Clause 26.6.4] allows welding in rebars. ACI also suggest a provision in AWS D1.4 cover aspects of welding reinforcing bars, including criteria to qualify welding procedures.
To know about BUTT JOINT!
· Butt Joint is a special type of weld in which no filler material is used i.e., Self-material is used to join rebars. While in other welding filler material is used which strength is less than TMT bar.
· In Butt joint, two rebar are joined by placing their ends together and then performing the welding operation.
· The whole process of Butt Joint takes hardily 2 minutes for a skilled person.
Technical specification:
· IS 9417:2018 [Clause 10.1.1] In high strength deformed bars shall be used either butt joint or lap joint.
· [Clause: 10.1.2] Bars of unequal diameter may be used in butt joint, the difference in diameter of bars shall not exceed 5mm.
· [Clause 10.2.1] butt joint adopted when a large number of joints has to done at same place.
Working principle:
· Basic concept of Butt Joint method “Resistance to Current Flow”. In this process high electric current is allowed to flow through rebar due to resistance to current flow a large amount of heat is generated at the intersection (Joule’s Heating Effect), which melt the parent rebar. When sufficient heat is generated in both rebar then this rebar is push towards each other to join them. After that the joint is allowed to cool down to develop strength.
Where: H = Heat generated
I = Current in Ampere
R = Resistance(Ω)
T = Time (Seconds)
Procedure:
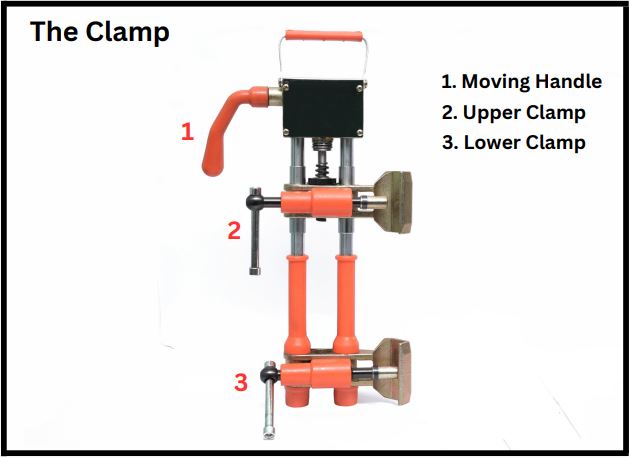
The Clamp:
· During the whole process of Butt Joint, we need to hold the both bars in position.
· Clamp has special arrangement to move the bar vertically up or down.
· Hold the both rebars in position.
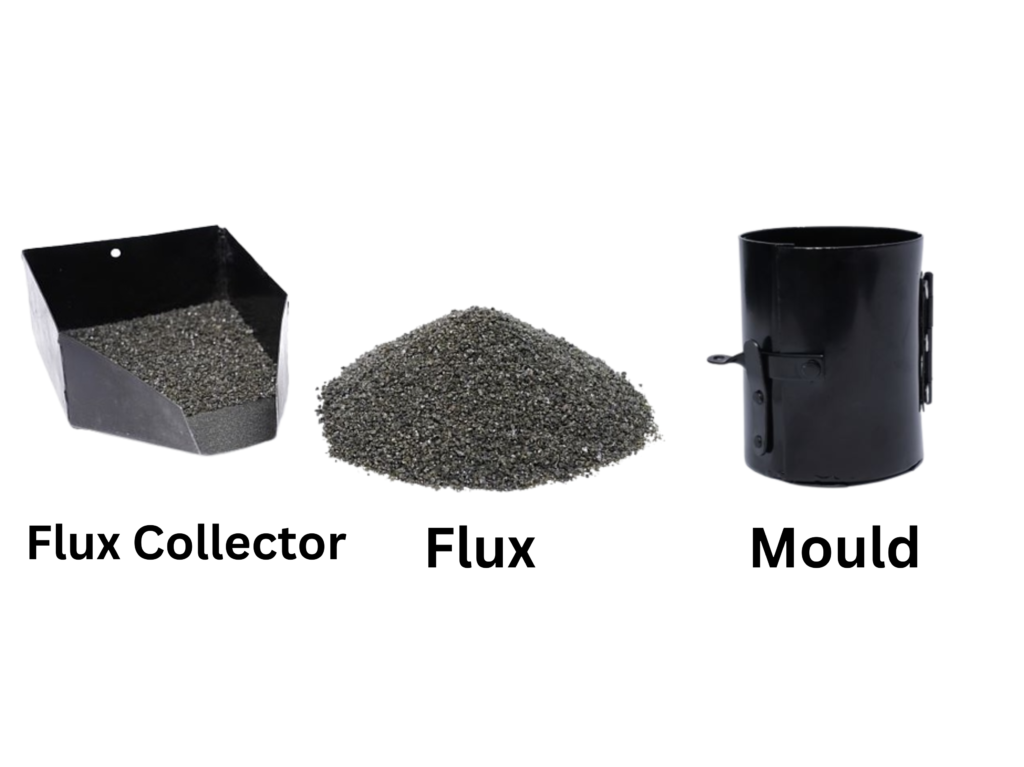
· Hold the inert material around the joint.
Flux material:
· It is reacting with oxides and turns to slag formation and make a protective layer on molten metal. It produces a gaseous shield to prevent contamination and act as scavengers to reduce oxides. It also influences shape of Butt joint bed during solidification.
Function of flux:
1. Deoxidation
2. Slag formation
3. Arc stability
4. Increase Butt Joint strength

Chemical Composition:
| Rebar Size (mm) | Per Joint Cost (₹) |
| 12 | 32 |
| 16 | 77 |
| 20 | 151 |
| 25 | 294 |
| 32 | 616 |
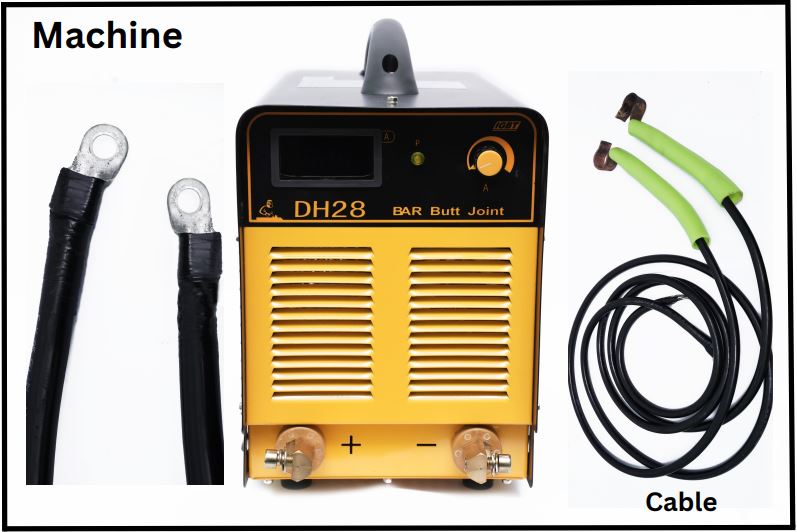
Butt Joint Machine:
· The steel bar electro slag pressure butt joint machine is a high-tech product, inverter and microcomputer control technology.
· It enhanced butt joint quality, improve production efficiency and has unique butt joint process.
· It has temperature sensor detecting the cooling, better arc ignition and stability.
· Machine design is compact, light in weight, small in size, easy to move and save working time.

Technical Benefits:
· Like rebar coupler, Butt joint can be used in any zone of column like A-Zone.
· Each Staggering can be easily maintained in column using butt joint.
· Eliminate joggling (1:6 slope) problem in rebars.
· Butt joint eliminates concrete dependency of bars in column.
Conclusion
Butt Joint technology is a superior alternative to overlapping in the construction industry. it’s reinforcement bars have limitations in terms of time consumption and reduced column size. on the other hand, eliminates the need for filler material, cutting rebars at specific angles, and reduces overall construction time. It is endorsed by industry codes like IS 9417:2018 and ACI-318-19, involving joining rebars by placing their ends together and using welding to create a strong joint. Butt Joint machines with advanced features are available for efficient and high-quality results.