COLD FORGING: An Effective Solution of HEAT ZONE in Butt Joint Technology
The process of Cold forging TMT bars involves applying pressure to a metal, which results in the material being shaped into a desired form. Use of Cold forged TMT bar instead of non-forged bar in butt joint can have positive impact on strength of joint. Cold forging is an important process in TMT bars that results in a material with superior properties compared to Non-Forged TMT bars. By the use of Cold Forged TMT bar in Butt Joint we can make stronger and durable joint which can improve overall strength of reinforced concrete structure.
What is the PURPOSE of Cold Forging?
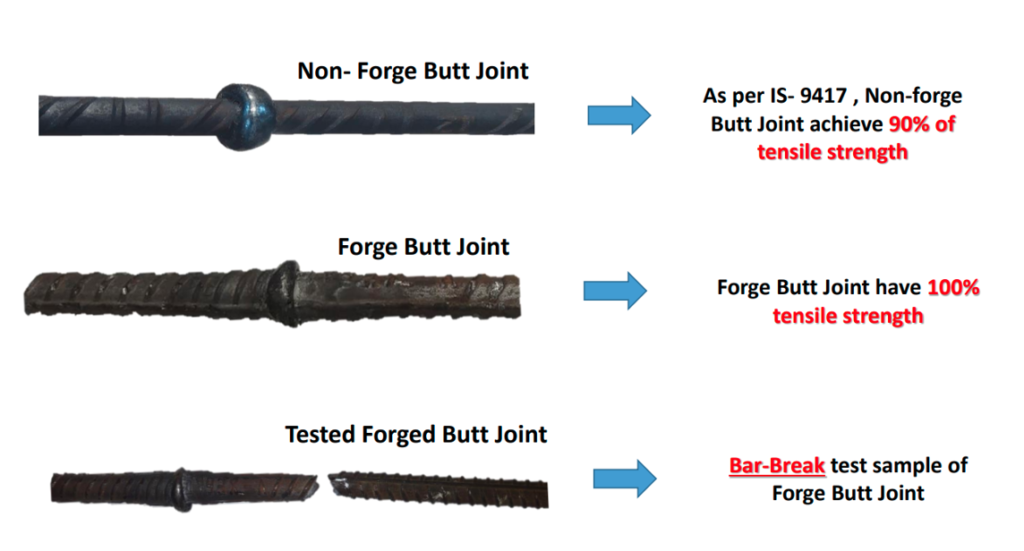
Forged Butt Joint & Non-Forged Butt Joint

Use of Cold forged TMT bars instead of non-Forged bars in Butt Joint can have positive impact on strength of joint. The material is compressed during the forging process, which causes the grains to deform and align in the direction of the material flow. As a result, the pattern of the grains becomes elongated and flattened along the direction of the flow, which might increase the material’s Strength and Toughness.
Effect of Cold forging on TMT bar structure:
Compared to other manufacturing processes like machining and casting, Cold forging is often considered superior. This is because forging improves grain structure and develops Ideal Grain Flow in components.
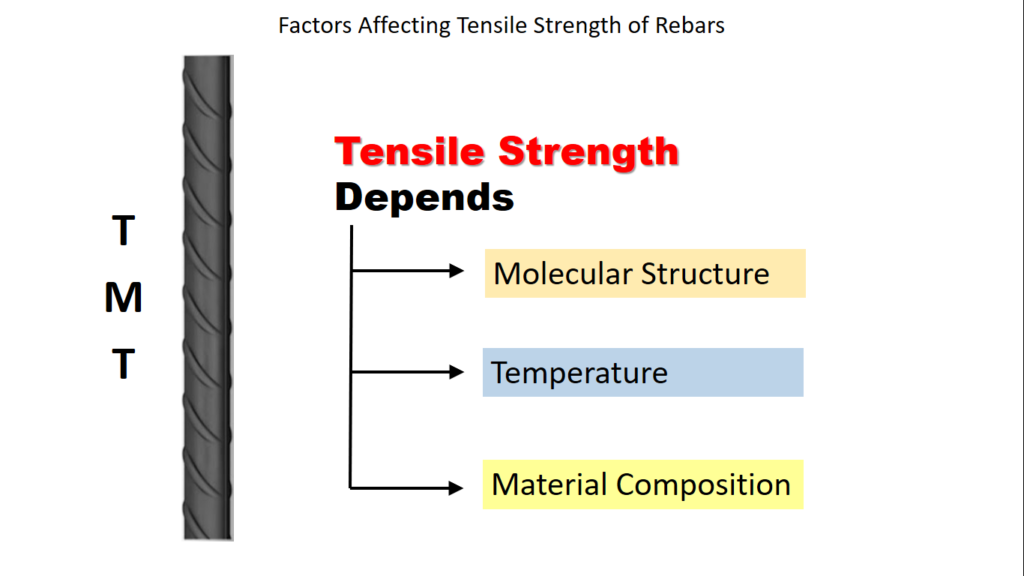
Factors Affect Tensile Strength of Steel:
- Molecular Structure
- Temperature
- Composition, the composition of the materials is also greatly responsible for the tensile strength of the materials.
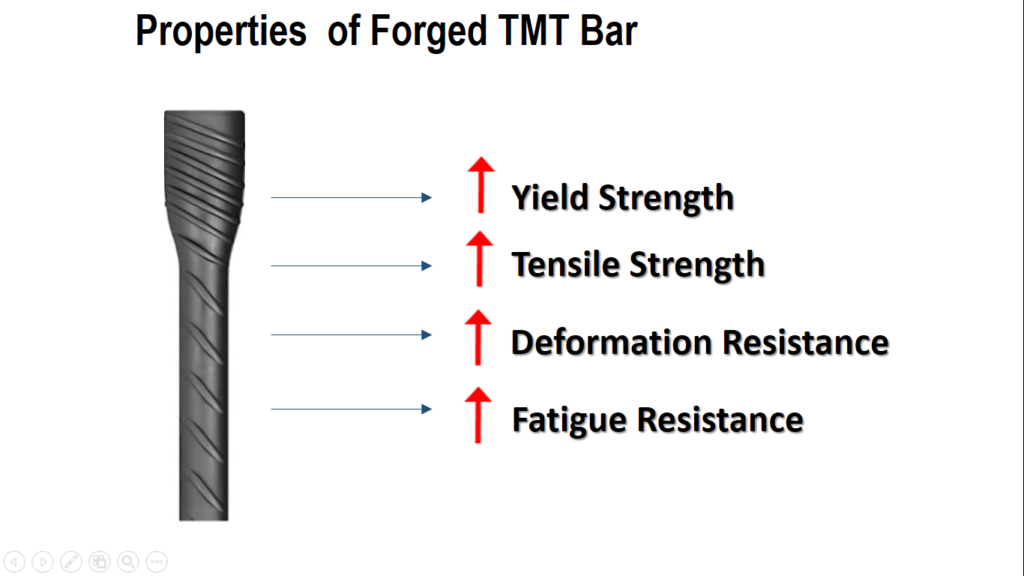
vProperty of Cold forged TMT bar:
- The Cold forging process results in a material that has a Higher Yield Strength, & Tensile Strength.
- Cold forged TMT bars more resistant to deformation and damage.
- Cold Forged parts had a 26% higher tensile strength than the cast parts. This means you can have stronger shackles at a lower part weight. Forged parts have a 37% higher fatigue strength.
- The Cold forging process also helps to eliminate any internal defects and improve the grain structure of the material, resulting in a more uniform and consistent product.
Conclusion